The German cipher machine Enigma This webpage was created after an interesting study tour to London and Bletchley Park As a high school teacher and mathematician from Denmark, I normally only write in my native language, which is DanishENIGMA CODE CODES AND CYPHERS BLETCHLEY PARK NAVAL ENIGMA The first wartime naval Enigma machine (M3) was identical to the model used by the German Army and Air Force, but it was issued with additional rotors, VI, VII and VIII, which were reserved for the Kriegsmarine (German Navy) However, the Kriegsmarine also employed codebooks toA team of Polish cryptanalysts was the first to break Enigma codes as early as 1932, however the German used more advanced Enigma machines making it virtually impossible to break the Enigma code using traditional methods In 1939, with the prospect of war, the Poles decided to share their findings with the British
Enigma Procedure
German enigma code translator
German enigma code translator-Enigma Machine Cipher Decoder, Encoder, Solver, Translato Hex Code Translator (Beta) Convert text to Hexadecimal Code See also Morse code Translator, Binary Code Translator, QR Code Generator Enigma and the Bombe The main focus of Turing's work at Bletchley was in cracking the 'Enigma' code A German Enigma machine codebook designed for use aboard a second world war Uboat has smashed its estimate at auction Valued at $30,000, it sold for a phenomenal $225,000 That's a world record for an Enigma code book at auction The previous highest figure was the $146,500 paid for a Kurzsignalheft (Short signal book) in 14



Enigma Machine Wikipedia
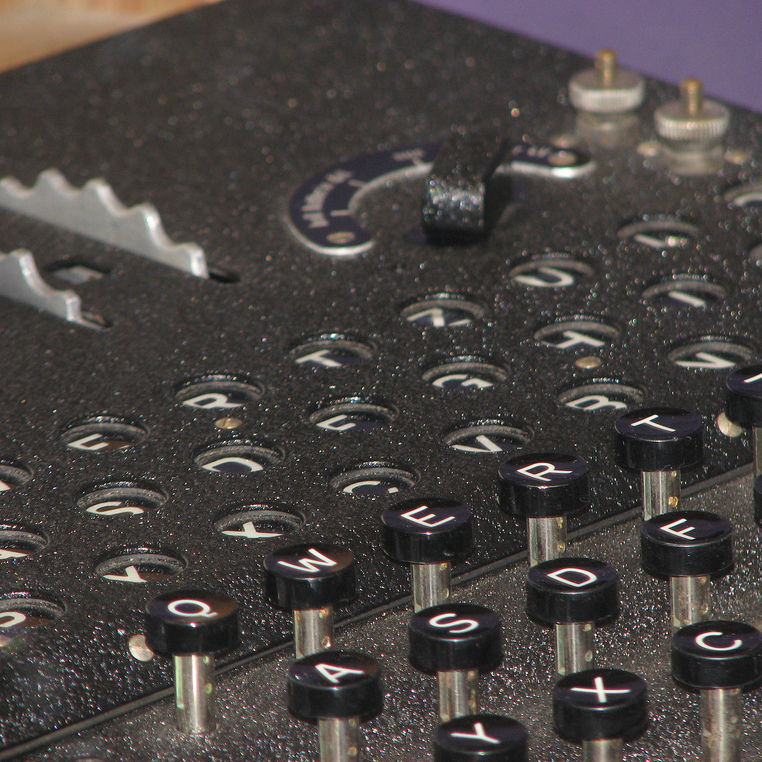
An Enigma machine is a famous encryption machine used by the Germans during WWII to transmit coded messages An Enigma machine allows for billions and billions of ways to encode a message, making it incredibly difficult for other nations to crack German codes during the war — for a time the code seemed unbreakable Alan Turing and other researchers exploited aHow To Use The Enigma Machine The Enigma Machine is an accurate simulation of the M3 Enigma cipher machine used by the German Navy during the Second World War This particular Enigma model utilised 3 rotors (selected from a total of 8), and had a choice of 2 reflectors Other Enigmas of the time used more rotors and had extra reflectors availableMachinery needed to crack the codes helped to bring an end to the Third Reich The British worked to break the Enigma at Bletchley Park in England The code breakers were organized into Huts These Huts worked in pairs and were known only by their numbers for security reasons Huts 3 and 6 worked together on deciphering messages from the German
DCode can code/decoder 3 enigma machines (Wehrmacht/Luftwaffe with 3 rotors and Kriegsmarine with 3 or 4 rotors) Each model has its own rotos and reflectors Rotors have notches For rotor I, going from Q to R advances the next rotor, notches depends on each rotors and cannot be configured Rotors can be mounted in any order but Beta and GammaTuring was a bright mathematician He went to both Princeton andThis version of cryptii is no longer under active development Find the latest version on cryptiicom Cryptii is an OpenSource web application under the MIT license where you can encode and decode between different format
Morse Code Translator is a translator that lets anyone translate text to Morse code and decode Morse code to text easily With the online Morse code translator, anyone can convert any plain text in English or whatever language to Morse code and vice versaENIGMA CIPHER MACHINE SIMULATOR 705 About the Enigma Simulator The German Enigma machine is the most famous example of the battle between codemakers and codebreakers Never before has the fate of so many lives been so influenced by one cryptographic machine, as the Enigma did in the Second World War The enigma machine was used in World War II to encrypt secret messages The Enigma machines are a series of electromechanical rotor cipher machines The first machines were invented at the end of World War I by German engineer Arthur Scherbius and were mainly used to protect commercial, diplomatic and military communication Enigma machines became




Enigma Encryption Machines Used By The Nazis Could Help Create Fraud Proof Bank Cards Daily Mail Online




Volume 40 3 Translate The Site Magazine
Cryptanalytic success in World War II was the breaking of the German ENIGMA machine This cryptodevice was used by all of the German armed forces as the primary cryptosystem for all units below Army level or the equivalent As DDay approached, other German cryptodevices, the SZ42 and the various T52 machines, assumed great Breaking the German Enigma Code and Lorenz ciphers played a key role in the UK's fight against Germany It helped the Allies score warchanging wins in Europe – and later the Pacific – giving them a necessary edge against the Nazis Bletchley Park, 1926Hofzumahaus fzjuelichde fzjuelichde Veils rise and fall like curtains, scattering the breath of the performers secrets are as if enveloped in shadows, in a fragile, quivering zone, glowing in subdued, iridescent colors, drifting past like fog, like something that although it



2



2
The Enigma was an encryption machine famously used by the German military during World War 2 The power of the Enigma came from being simple for the operator to use but difficult to determine the encrypted letter for any input letter The number of possible ways to jumble a message through an Enigma was nearly 159 quintillion Thanks to incredibleEnigma translation in English German Reverso dictionary, see also 'enigmatic',enigmatically',enema',Englishman', examples, definition, conjugationEnigma, device used by the German military to encode strategic messages before and during World War II The Enigma code was first broken by the Poles in the early 1930s In 1939 the Poles turned their information over to the British, who set up the codebreaking group Ultra, under mathematician Alan M Turing




Enigma Cipher Machines High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




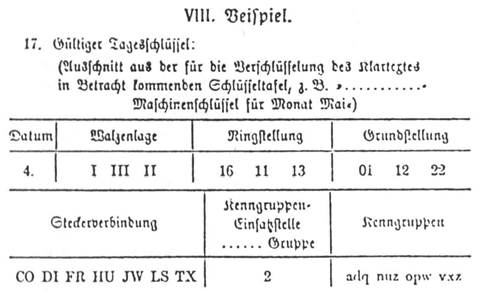
Enigma Daily Settings Generator 101 Computing
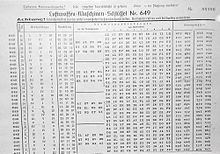
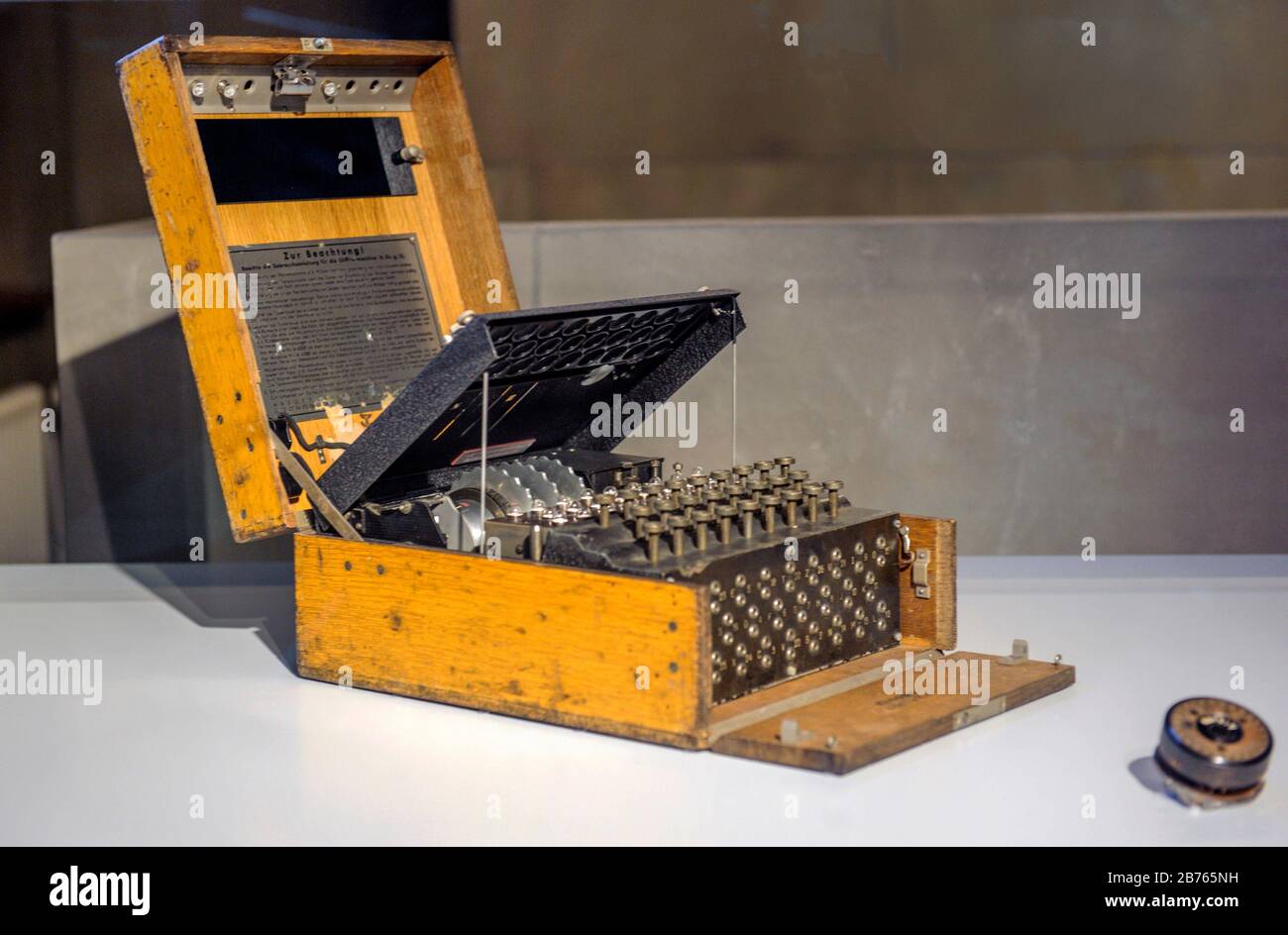
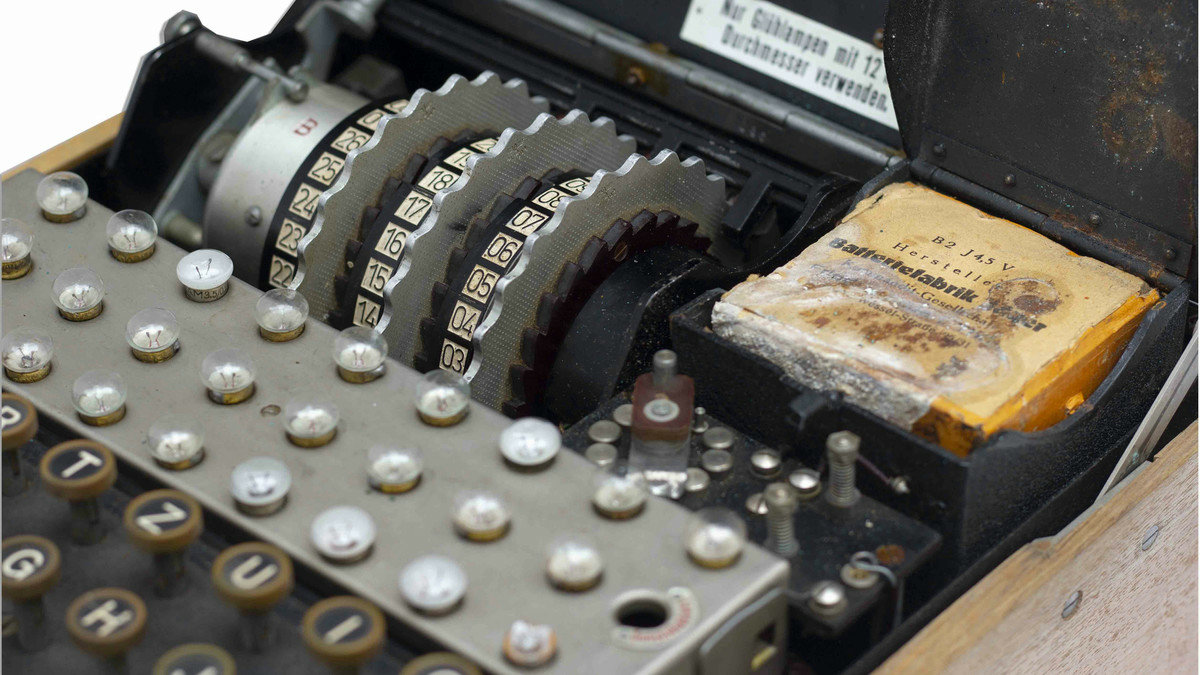
The Navajo code talkers As you will discover in this chapter, cryptography was one of the earliest applications of modern computing During World War II, a codebreaking team in England, building on earlier work carried out in Poland, developed specialized hardware that was able to break the German Enigma codeThe Service Enigma Machine Enigma I (Roman '1') is an electromechanical cipher machine developed in 1927/29 by Chriffriermaschinen AG (later Heimsoeth und Rinke) In Berlin (Germany) for the German Army (Reichswehr, later Wehrmacht) 1 and introduced in 1932 It is based on the chassis of the commercial Enigma D, but has a fixed reflector, and a plugboard (Steckerbrett) atWith this Enigma Codebook Tool, you can create code sheets with key settings for different models of German Enigma cipher machines These sheets contain all necessary information to setup your Enigma The program can create, show, save and print a single code sheet, valid for one month, or a complete year This tool can create codebooks for the



Teaching History With 100 Objects Enigma Cipher Machine
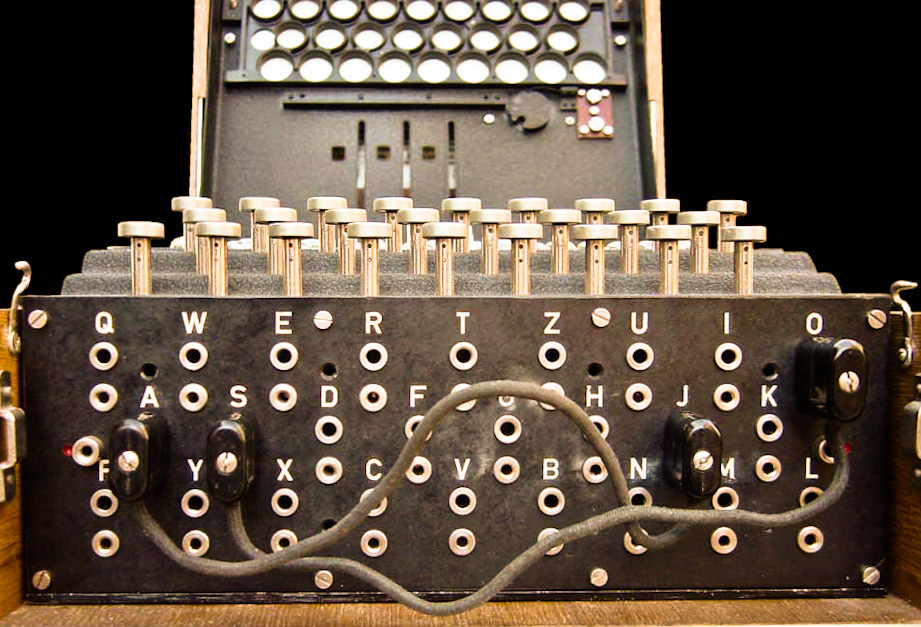




The Enigma Machine A Window Into The History Of Encryption
Can Hallworth Crack Trump Code?The German military caught interest, and commercial production was stopped in 1923 6 The initial idea was pretty much based on the well known Caesar cipher 7, a monoalphabetic substitution Each letter is substituted for example by its nth neighbor in the alphabet Code for an Enigma simulation is incorporated into a program of twoThe Public Enigma is free to download and can be used for noncommercial or educational purposes The simulator contains 13 Enigma variants developed over a 19 year period () They are constructed and wired in the exact same way as the actual Enigma's




German Enigma Code Translator 11 21



Enigma Codeproject
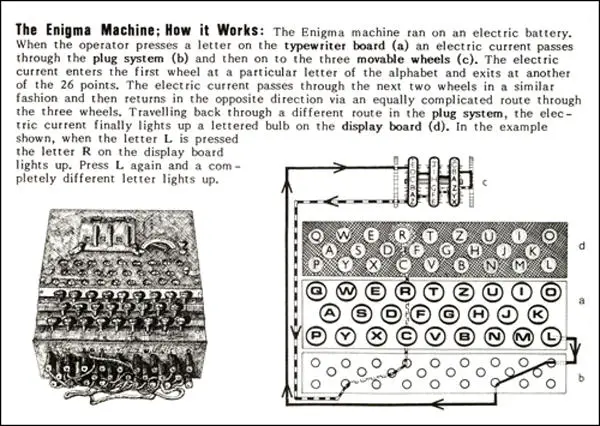
The ENIGMA machine, shown in the figure below with its cover closed, is a rotor cryptomachine It consists of a typewriter, a set of lamps labeled with letters in front of the typewriter keys, a set of rotors (partially hidden by the cover) in front of the lamps, and a plugboard on the front vertical wall of the boxThe Enigma machines were a series of electromechanical rotor cipher machines developed and used in the early to midtwentieth century to protect commercial, diplomatic and military communication Enigma was invented by the German engineer Arthur Scherbius at the end of World War I Early models were used commercially from the early 19s, and adopted by military Using this method of encryption, it was possible to program the Enigma Machine in 158 quintillion (that's 158 followed by thirty zero's) different ways – and the machine only stayed set with one code for 24 hours After the 24 hours, the machine would be reset by changing the rotors and plug board, and the code would change once again




How Do Archaeologists Crack The Code Of Dead Languages Discover Magazine



Enigma Procedure
Answer (1 of 3) You really have to think of the machine and the key at the same time The Germans never imagined that the machine was useful to the enemy without the key or the key without the machine The machine itself consisted of a keyboard, aEnigma's Secrets How it Worked and How the Code was Broken By way of introduction, see the Historical Background to Enigma and the Key Players Involved The Working Principle The Enigma machine basically provided a simple substitution of a plaintext symbol with a different ciphertext symbol generated by the machine What made the machine special however was thatThe plain text of the messages is of course in the German language, and may include abbreviations and conventions such as "X" for a space, "J" for a quotation mark or "Q" for the two characters "CH", so further interpretation and translation will be needed to produce an understandable message in English



Virginia Council Of Teachers Of Mathematics The Navajo Code Talkers Of World War Ii



2
Enigma This page uses JavaScript to simulate a threerotor Enigma machine;About Menu Toggle About Us;HII Philosophy of Coaching;




Enigma The German Cipher Machine



Enigma And A Way To Its Decryption
Translation of "EnigmaCode" in English Enigma Enigma Code code coding passcode cipher coded Other translations Wenn Sie nach diesem Tutorial werden Sie nun in der Lage zu verstehen, und EnigmaCode Api If you followed this tutorial you The enigma machine was used in World War II to encrypt secret messagesThe Enigma machines are a series of electromechanical rotor cipher machines The first machines were invented at the end of World War I by German engineer Arthur Scherbius and were mainly used to protect commercial, diplomatic and military communication Enigma machines became Associated with breaking the highly complex German Enigma code, allied translators and codebreakers also worked together to break the Lorenz cypher that was used for messages between leading members of the Nazi regime and the army Their work was classified as "Ultra" secret, a new category ranking above the traditional "Top Secret"



Enigma Procedure




Breaking The German Enigma Code Cspan3 January 1 21 1 25pm 3 05pm Est Free Borrow Streaming Internet Archive
The number "65" represents the number of letters in the actual message, so the Radio Operator and Enigma Decoder can confirm they have the entire message The "=" are just place holders, much like a STOP in a Telegram or, in the case of Enigma, an "X" You'll find these throughout the body of the message FEW GHT =The Enigma cipher was a field cipher used by the Germans during World War II The Enigma is one of the better known historical encryption machines, and it actually refers to a range of similar cipher machines The first Enigma machine was invented by a German engineer named Arthur Scherbius at the end of the first world war1 The language is known as "linear B" and it predates the Greek alphabet and so most historians agreed it was probably a separate language altogether However, decoders who had worked on cracking the German Enigma code during World War II were able to decipher linear B by assuming that it was in fact an ancestor of Greek




Enigma Settings In Czech Translation Examples Of Use Enigma Settings In A Sentence In English
:strip_icc()/pic2372547.png)



Enigma A Full English Translation Boardgamegeek
Hacking the Nazis The secret story of the women who broke Hitler's codes By Nick Heath on Of the 10,000plus staff at the Government Code and Cypher School during World War II Dear code breaker, I am contacting you from Bletchley Park as we are intercepting an increased volume of encrypted radio signals We are working day and night to break the enigma codes that the German Navy are updating every day The German UBoats are operating in the Atlantic Ocean and are causing major casualties by sinking not only military ships from the Royal In June 1931 the French were approached by a German spy HansThilo Schmidt ("Asche") who was an employee at Armed Forces' cryptographic headquarters and provided them with the book of system code breaking keys along with many technical details of how Enigma was constructed and worked




Enigma Machine




Ultra Wikipedia
The Enigma machine is a cipher device developed and used in the early to midth century to protect commercial, diplomatic, and military communication It was employed extensively by Nazi Germany during World War II, in all branches of the German militaryThe Germans believed, erroneously, that use of the Enigma machine enabled them to communicate securely and thusEnigma and the Bombe The main focus of Turing's work at Bletchley was in cracking the 'Enigma' code The Enigma was a type of enciphering machine used by the German armed forces to send messages securely Although Polish mathematicians had worked out how to read Enigma messages and had shared this information with the British, theSquadrons of German Uboats were swarming in the Atlantic ocean hunting down Atlantic convoys bringing supplies



The Cryptological Origins Of Machine Translation Amodern



Virginia Council Of Teachers Of Mathematics The Navajo Code Talkers Of World War Ii
Wednesday 0604PM To paraphrase Winston Churchill, working out how to climb up the snooker rankings is a riddle, wrapped in a mystery, inside an enigma Steven Hallworth hopes he is on that journey and faces one of the biggest tests of his career tonight when he takes on world number one Judd Trump inCryptiiText to Enigma Cryptiiv2 Cryptii Convert, encode, encrypt, decode and decrypt your content online Attention!The Enigma cipher machine is well known for the vital role it played during WWII Alan Turing and his attempts to crack the Enigma machine code changed history Nevertheless, many messages could not be decrypted until today




Pin On Birth Of Computers In Revolution Exhibition



Enigma Machine
Until the debut of "The Imitation Game," an Oscarnominated film Alan Turing's name wasn't widely known Alan is the man behind the cracking of the Enigma code, and his role in the ending of World War II cannot be underestimated Who Was Alan Turing? How the Allies cracked the Enigma Code It is the peak of World War II Wolf packs;The type used by the German army during World War II Enigma machines were used to encrypt messages by exchanging letters in the plaintext to produce the ciphertext in a manner far more complex than the standard Caesar Shift substitution cipher (ie if you press the same letter on the keyboard twice,




Bletchley Park The Nerve Center Of British World War Ii Code Breaking Cgtn
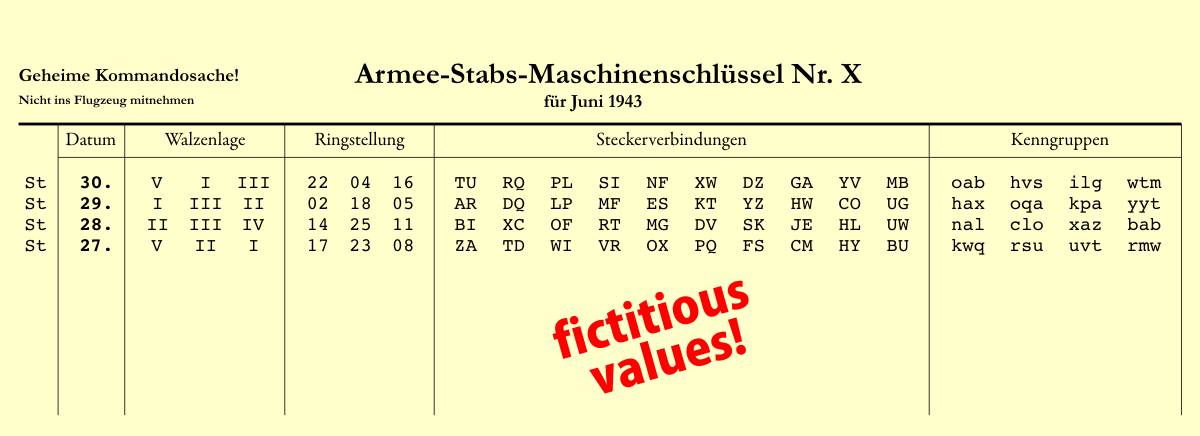



Enigma The German Cipher Machine




Christos Military And Intelligence Corner Naval Enigma Compromise And The Spy In The United States Department Of The Navy
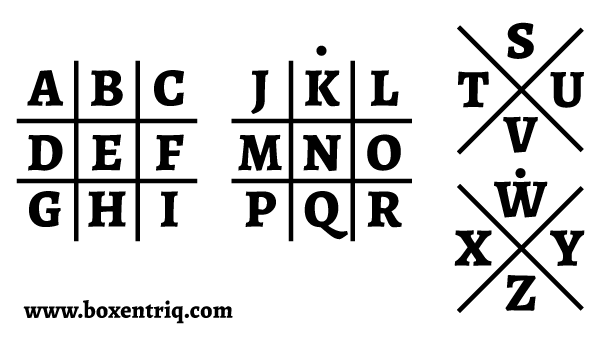



Pigpen Cipher Online Tool Boxentriq



Polish Mathematicians And Cracking The Enigma European Studies Blog




Christos Military And Intelligence Corner The Compromise Of The Swiss Diplomatic Enigma K Cipher Machine In Wwii




How To Build An Enigma Machine Virtualisation In Python By Vasile Păpăluță Analytics Vidhya Medium




The German Enigma Cipher Machine Beginnings Success And Ultimate Failure Artech House Computer Security Brian J Winkel Cipher Deavors David Kahn Amazon Com Books




Enigma Machine Wikipedia
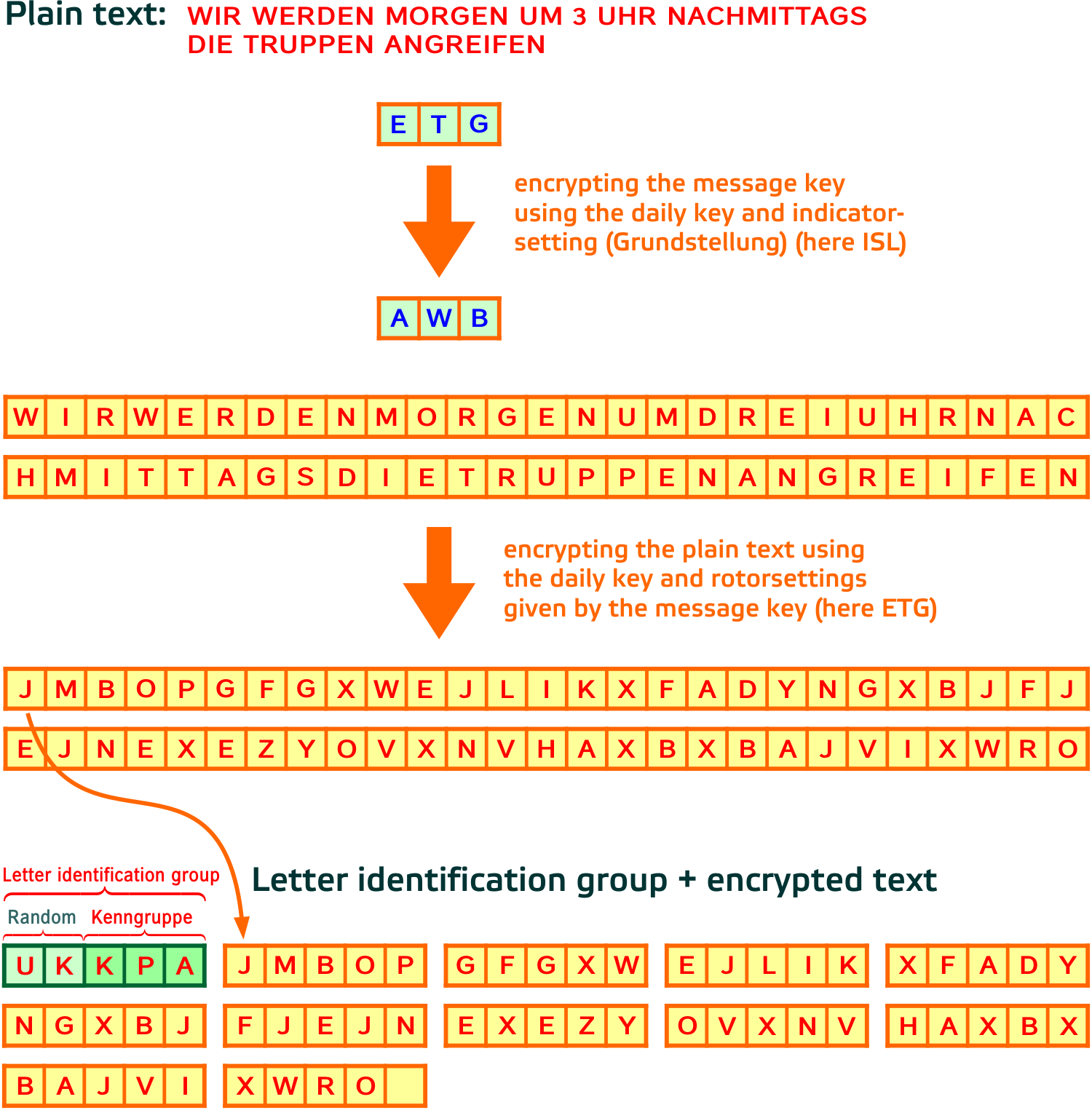



Enigma The German Cipher Machine



Enigma Procedure
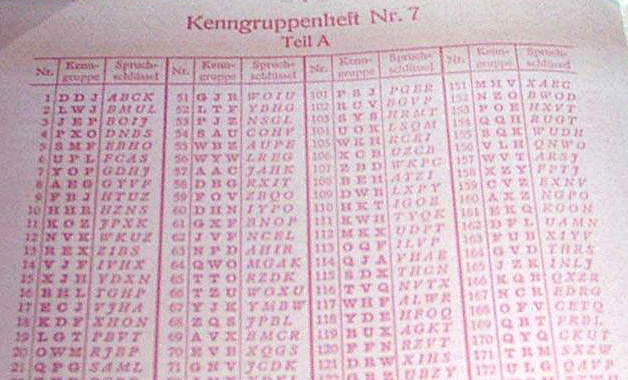



A Riddle Called Enigma



Enigma Procedure
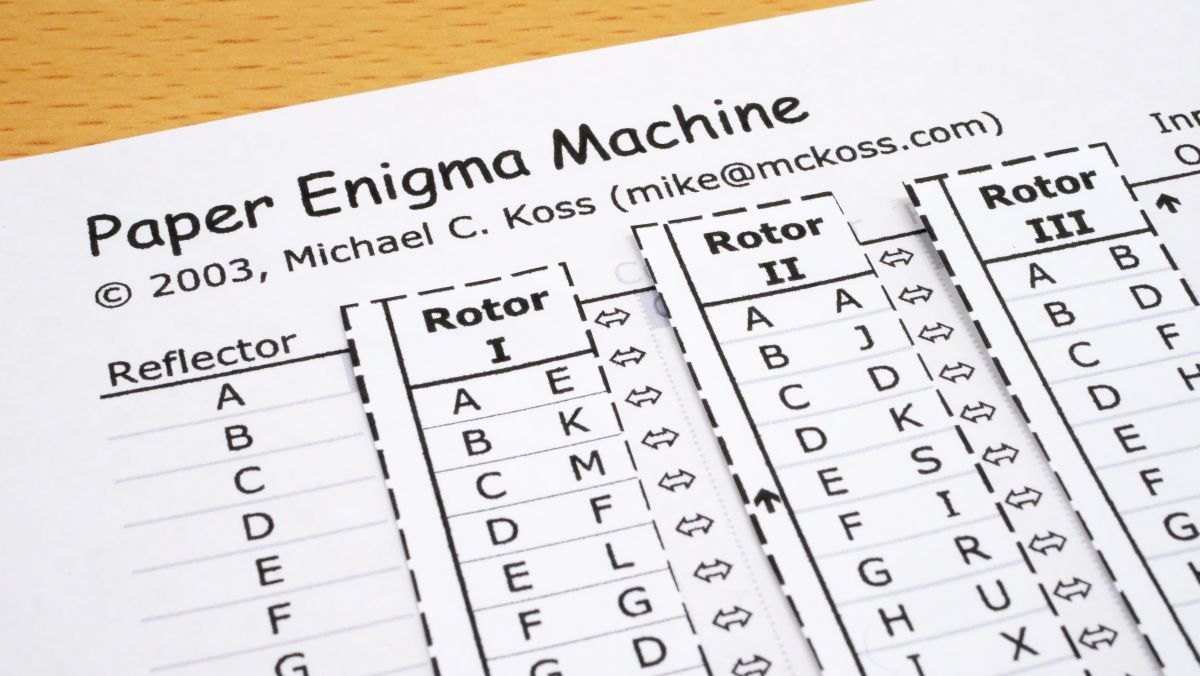



I Tried Using Paper Enigma Machine Which Can Reproduce Nazi Germany S Masterpiece Encryption Machine Enigma With Only One Sheet Of Paper Gigazine




Exploring The Enigma Plus Maths Org




Pdf Marian Fast Neural Machine Translation In C




Second World War Enigma Machine Enigma Rotor Details Cipher Diagram Calalog Second World War Calalog Png Pngegg
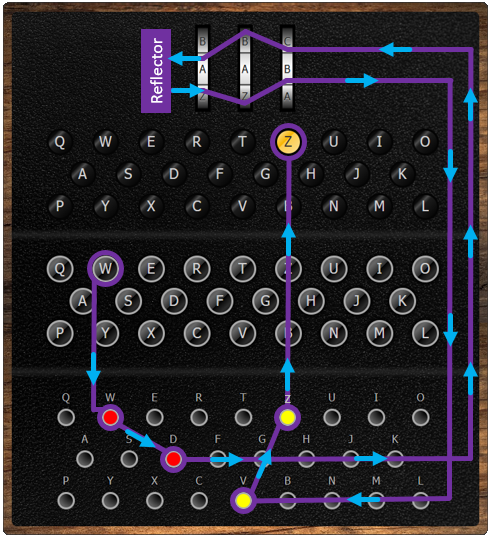



Enigma Encoder 101 Computing
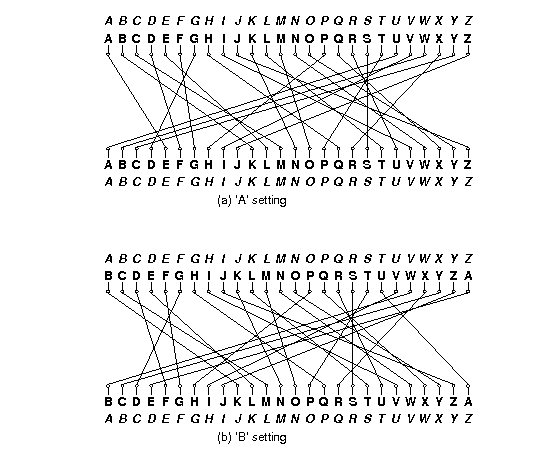



Project 1 Cs 61b Fall 19
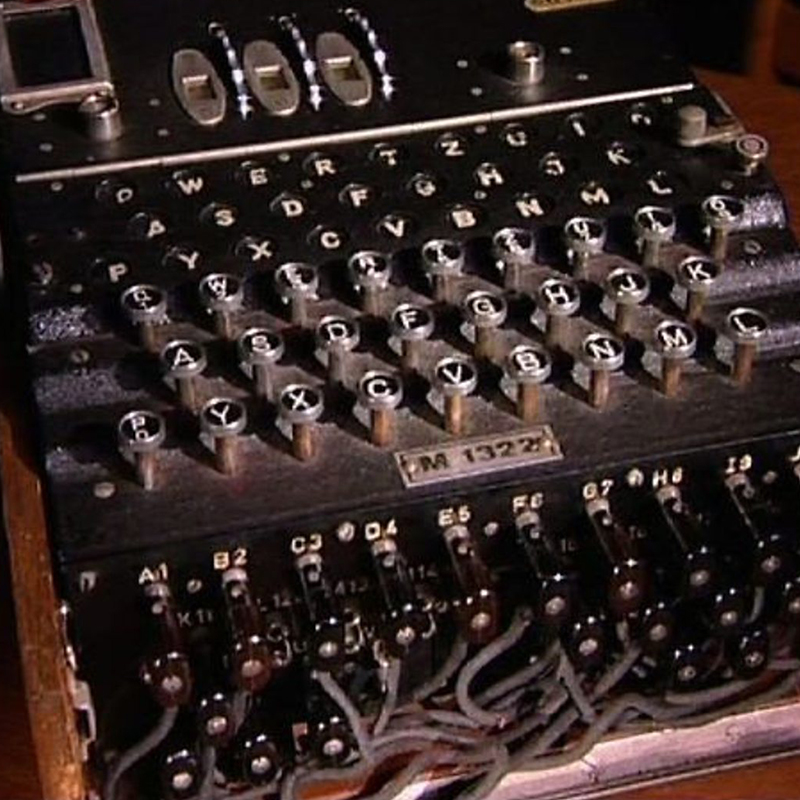




Science The Enigma Machine Swinemoor Primary School
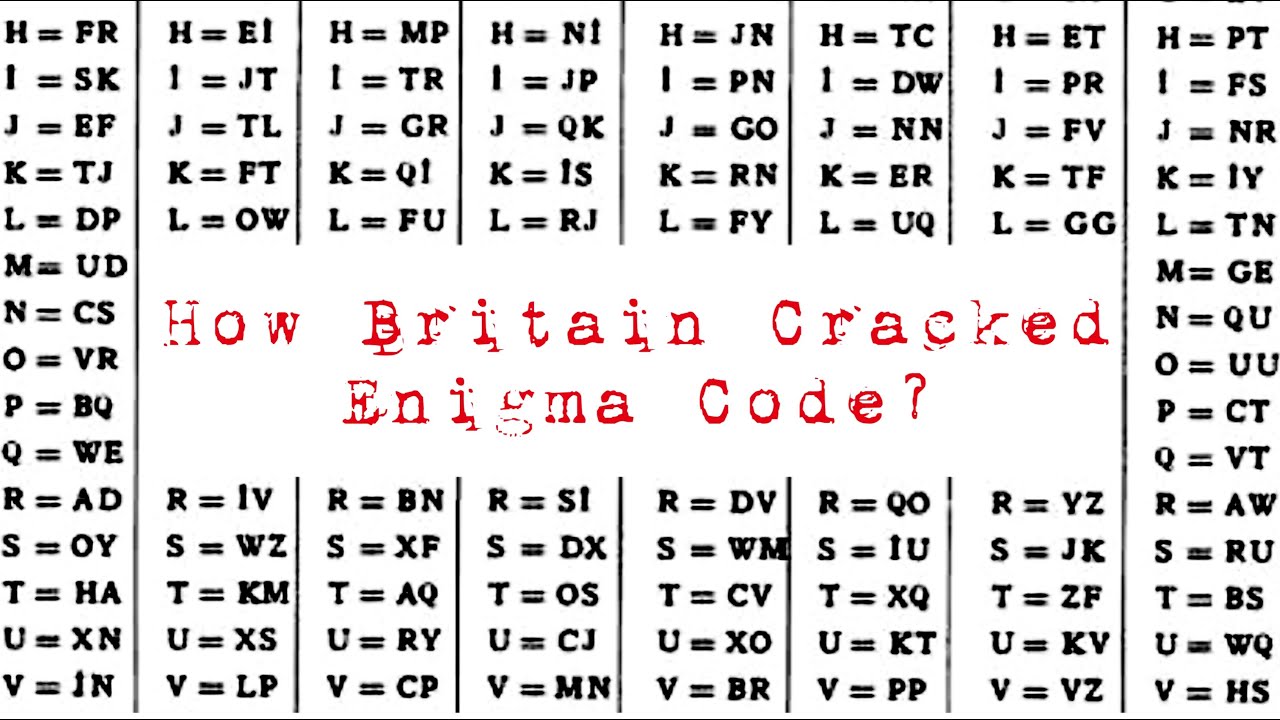



How The Allies Cracked The Enigma Code By Karthick Nambi Lessons From History Medium




German Enigma Code Translator 11 21
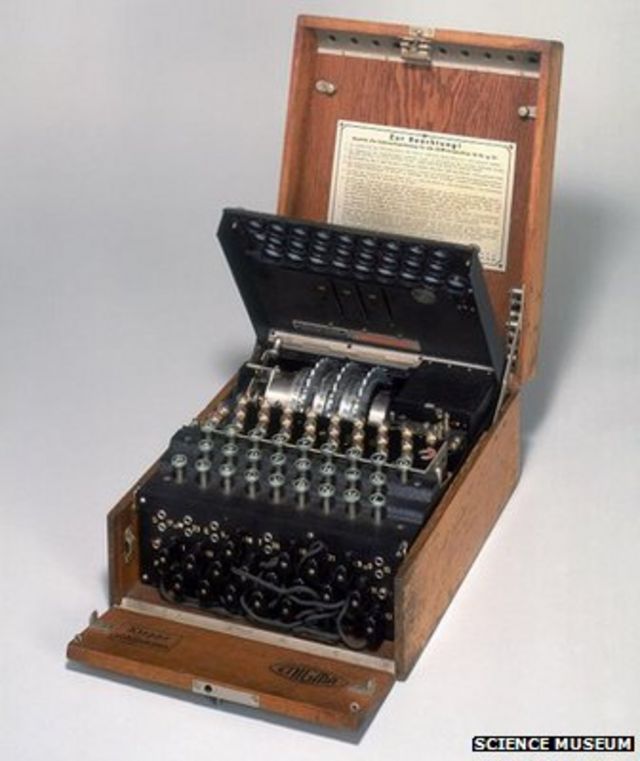




Alan Turing The Codebreaker Who Saved Millions Of Lives c News
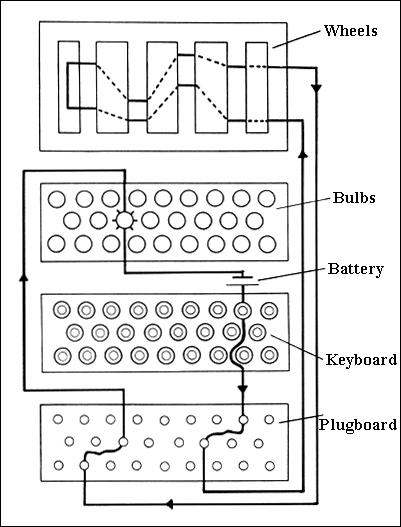



Enigma Machine




Gc5yp21 Enigma Unknown Cache In Texas United States Created By Manofsteel73




Solved Function Name Geheimferncipher Inputs 1 Char Chegg Com




Visiting World War Ii S Enigma Breaking Bletchley Park In England Stuff Co Nz




Enigma Definition Machine History Alan Turing Facts Britannica




An Entertaining History Of Translation Tech And Then Some Heretto




The Enigma Cipher Machine And Breaking The Enigma Code



Text To Enigma Cryptii
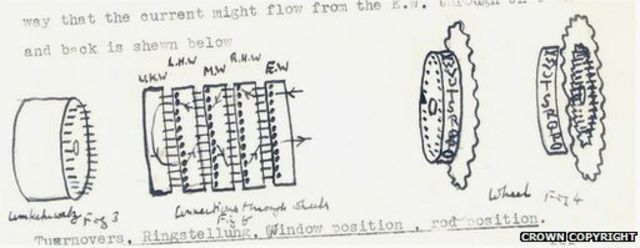



Alan Turing The Codebreaker Who Saved Millions Of Lives c News



3




Solved Function Name Geheimferncipher Inputs 1 Char Chegg Com




17 Content Strategy Trend The Rise Of The Machine Translation Scriptorium




Enigma Machine




How The Allies Cracked The Enigma Code By Karthick Nambi Lessons From History Medium



2




Celebrating Navajo Code Talkers Day Arizona Historical Society




Lecture On Naval Enigma Tony Sale




Cracking The Enigma Legion Magazine



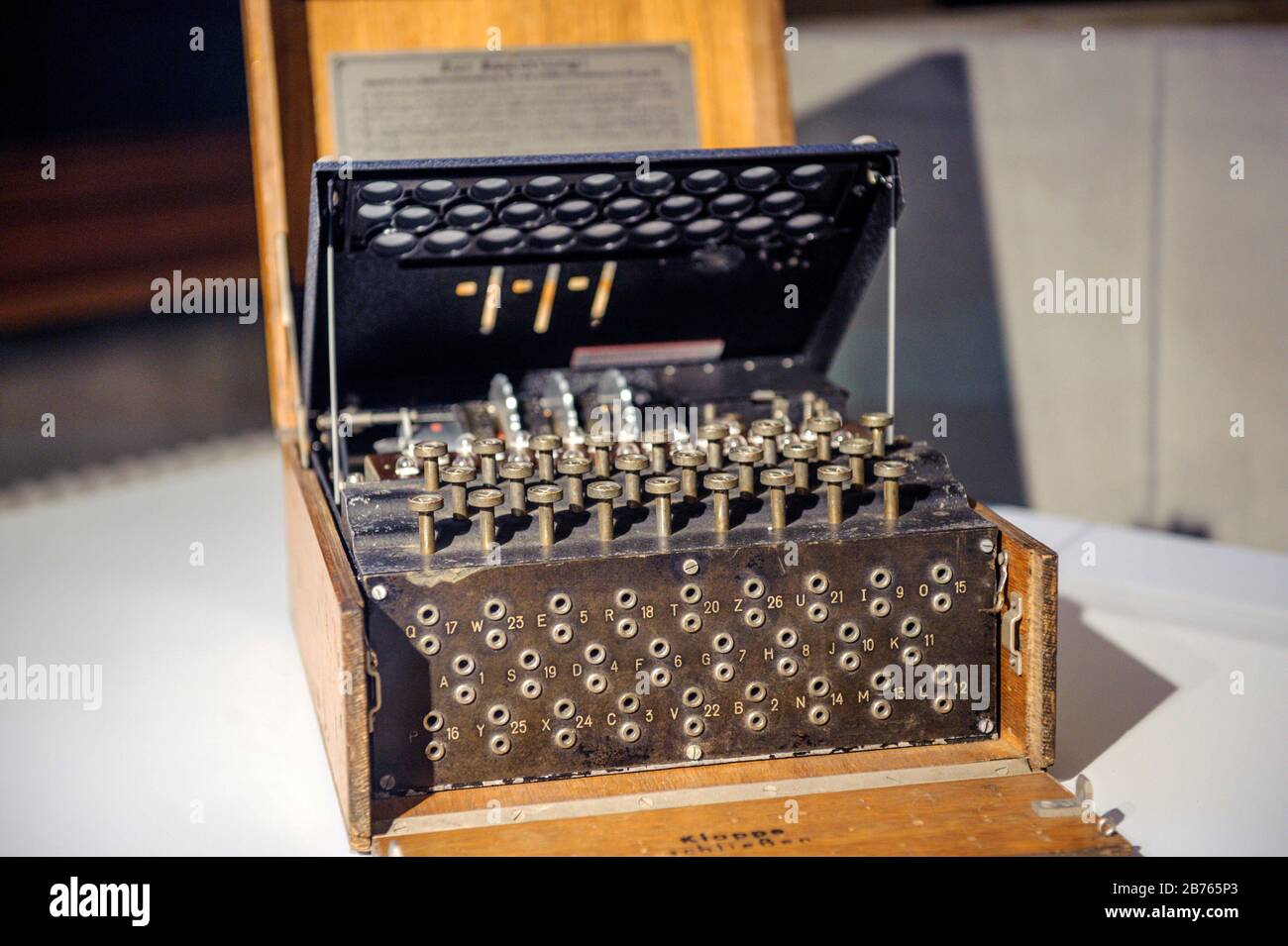
Enigma Wiring




Enigma Encryption Machine High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Enigma Machine Simulator Program About Code Name Verity Spies Etc Enigma Aspectos Historia



Breaking The German Enigma Code C Span Org



The Cryptography Enigma Simulator That The German Army Used In World War Ii Gigazine




Cipher Machine High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Enigma Machine Emulator 101 Computing




The German Enigma Cipher Machine Beginnings Success And Ultimate Failure Artech House Computer Security Brian J Winkel Cipher Deavors David Kahn Amazon Com Books




Cs 111 W Lab 7 The Enigma Machine Pair Programming



Enigma Procedure




Nazi Germany S Masterpiece Cryptograph Machine Enigma Box Manual With Beauty Item Appeared On Net Auction For 22 Million Yen Gigazine




Enigma Machine Wikiwand




Cracking The Code Mapping The History Of Machine Translation Straker Translations




Enigma Code Translator 11 21



1




Exploring The Enigma Plus Maths Org
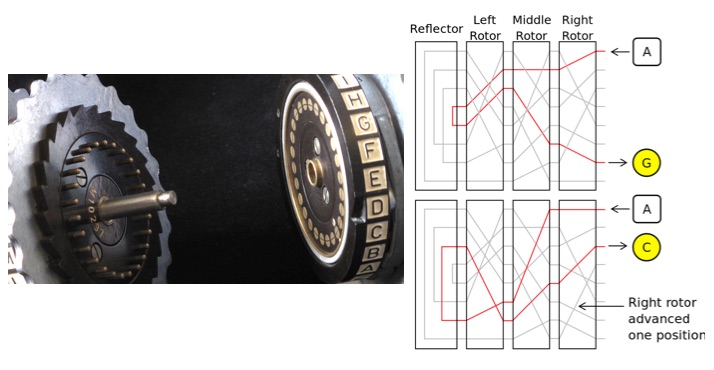



Q How Good Is The Enigma Code System Compared To Today S Publicly Available Cryptography Systems Ask A Mathematician Ask A Physicist




Enigma Machine By 101computing Net




Enigma Machine Wikipedia




Pin On Scientists




Enigma Machine Brilliant Math Science Wiki




How Did The Enigma Machine Work Computing The Guardian




German Enigma Code Translator 11 21




Enigma Machine Wikipedia




Cryptographic History Of Work On The German Naval Enigma
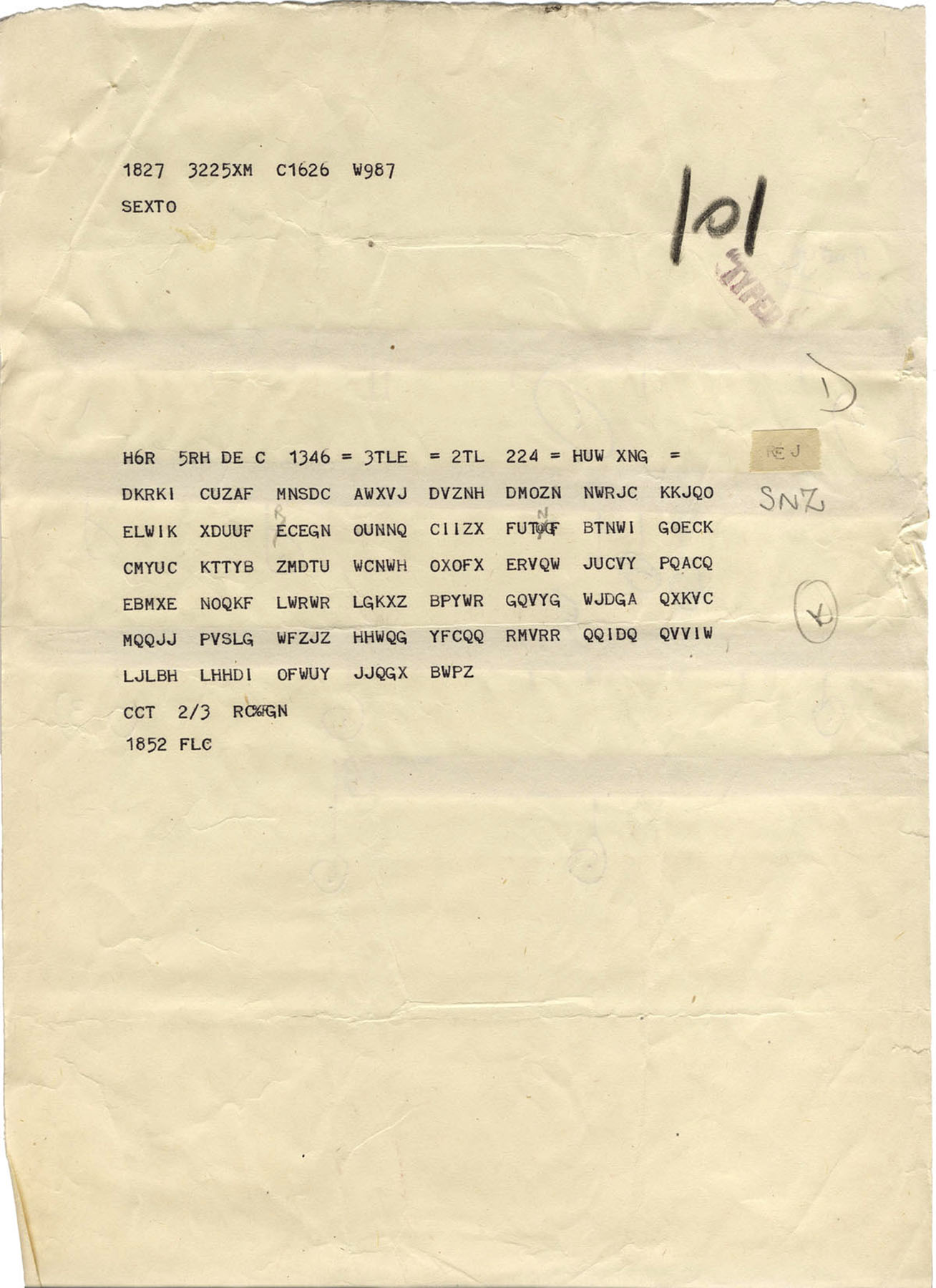



War Of Secrets Cryptology In Wwii National Museum Of The United States Air Force Display



Enigma Machine



Breaking The German Enigma Code C Span Org




Zygalski Sheets Wikipedia




Bonhams A Rare 1944 Edition Of The Kurzsignalheft Or Enigma Code Book Circa 1944 12 X 8 1 2 In 30 4 X 21 5 Cm




Cryptanalysis Of The Enigma Wikipedia
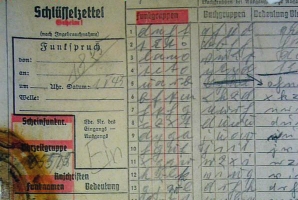



Enigma M4 Message P



Enigma Key Book Photo From Authentic German Codebook From Before Download Scientific Diagram



3



1



Ams Feature Column More Enigma




How Alan Turing Cracked The Enigma Code Imperial War Museums



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿